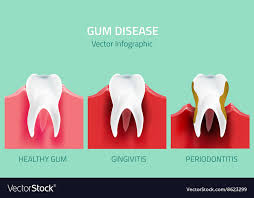
In its early stages, gum disease – known as gingivitis is reversible. Gingivitis is caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on your teeth and gums causing gum irritation and inflammation resulting in swollen and tender gums that bleed when brushing and flossing. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, can range from mild gingivitis to more severe periodontitis.
Periodontitis is the advanced stage of gum disease and is the leading cause of adult tooth loss. It is estimated that a majority of adults will be affected by some form of gum disease at some point in their lifetime, making the practice of preventive dentistry just as important for adults as it is for children.
Only through having your teeth professionally cleaned, a procedure called scaling and root planing, is it possible to remove the build-up of calculus (tartar) from your tooth surface above and below your gum-line, as this cannot be achieved by brushing and flossing.
Another side effect of gum disease and perhaps the most embarrassing, which many sufferers are unaware of, is constant bad breath. Clinically known as halitosis, it is caused by the accumulation of bacteria in your mouth and made worse by poor oral hygiene, tooth decay and gum disease producing a constant odour.
Regular dental check-ups will help prevent gum disease becoming advanced gum disease.
How is Gum Disease treated?
Treatment typically involves a combination of professional dental care and diligent oral hygiene practices at home.
Professional Cleaning: Our dentists will perform a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing. This involves removing plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gumline, as well as smoothing out rough spots on the tooth roots to prevent bacteria from accumulating.
Medication: Antibacterial mouth rinses or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to help control infection and reduce inflammation. In some cases, oral antibiotics may be necessary to combat severe infection.
Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, improving diet, and managing conditions like diabetes can help improve gum health and prevent further progression of the disease.
Surgical Treatment: In advanced cases of periodontitis, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as flap surgery, bone or tissue grafts, and guided tissue regeneration can help repair damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
Ongoing Maintenance: Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for monitoring gum health and preventing recurrence of gum disease. Patients will also need to maintain good oral hygiene habits at home, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouthwash.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease are crucial for preventing irreversible damage and tooth loss. It’s essential to see a dentist at Boroondara Dental regularly for dental examinations and cleanings and to seek prompt treatment if signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or receding gums, are present.